Working on Sitecore development projects typically involves two key steps. The first is the installation or deployment of the Sitecore instance, followed by the implementation or solution development. For those familiar with Sitecore XP/XM, deploying a vanilla Sitecore instance using tools like SIF/SIA could be time-consuming, often taking several hours due to prerequisites such as setting up Solr, SQL, and more.
However, the introduction of Sitecore Experience Manager Cloud (XM Cloud) has revolutionized this process. XM Cloud serves as a fully managed, self-service deployment platform tailored for developers, effectively addressing the challenges of lengthy deployment times. It enables the deployment of a fresh Sitecore instance with a fully functional website in just a few clicks.
In this blog post, I'll demonstrate how to deploy a demo website on the Sitecore XM Cloud. Subsequently, in the next blog post, I'll illustrate how effortlessly you can configure your local app development environment for XM Cloud and run the Sitecore XM Cloud Demo on your development machine. Stay tuned!
To log into and use the XM cloud portal at https://portal.sitecorecloud.io, developers must meet the following requirements:
Sitecore Cloud User Account: Developers need to have a Sitecore cloud user account linked to the organization that owns the subscription to XM cloud.
Admin Role Assignment: Additionally, they must be assigned an admin role within Sitecore cloud for that specific organization.
Log in to GitHub: Go to GitHub and log in to your account.
Access Sitecore's Repository: Visit the Sitecore XM Cloud repository on GitHub. You can find it at Sitecore's GitHub by searching for the specific repository name.
Repository: Once you're on the repository page, click the button in the top right corner of the page. This action will create a copy of the repository in your GitHub account.
Confirm Location: GitHub will prompt you to select the account/organization where you want to fork the repository. Choose your account.
Wait for to Complete: GitHub will start creating a repository in your account. This process might take a few moments.
Access Your Repository: Once the forking process is complete, you'll be redirected to your own GitHub account, where you'll find the forked repository. You'll notice it has the same name as the original repository, but it's now under your account.
Now, you have successfully Sitecore XM Cloud repository to your own GitHub account. You can work on this repository, make changes, and even create pull requests back to the original repository if needed.
Deploying the website on XM Cloud involves a few steps:
Access XM Cloud Portal:
- Log in to the XM Cloud Portal at https://portal.sitecorecloud.io.
Navigate to Project Management:
- From the dashboard, locate and click on "Manage my project XM Cloud deploy app." This action will redirect you to the deployment dashboard at https://deploy.sitecorecloud.io/.
Create a New Project:
- On the deployment dashboard, click on "Create new project."
Choose Deployment Method:
- Select "Start from your existing XM Cloud code" as the deployment method and proceed by clicking "Next."
Following these steps should allow you to initiate the deployment process for the website on XM Cloud, leveraging the existing code present within the XM Cloud infrastructure. This process enables you to begin a new project using the codebase already available within your XM Cloud environment.
In the next step, you will need to create or select a GitHub connection. Follow these steps:
First-time Setup:
- If this is your initial setup, select "Create a new GitHub connection."
Existing Project Setup:
- If you've previously set up the project, choose an existing GitHub connection from the dropdown.
Example: Here, I am clicking on "Create a new GitHub connection."
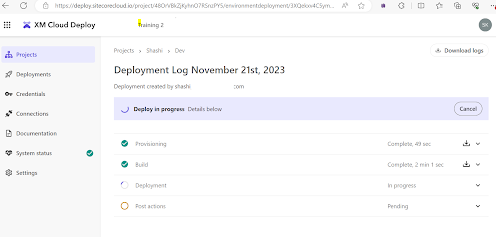
Deployment in Progress:
The project deployment process is underway. It may take a few minutes to complete.
Deployment Completed:
The deployment process has finished successfully, and your XM Cloud instance is now up and running.
Explore the XM Cloud Instance:
Access the Launchpad: Click on "Launchpad" to begin exploring your deployed instance.
Explore Different Features:
- Pages: Navigate through the Pages section.
- Content Editor: Access and modify content using the Content Editor.
- Experience Editor: Experiment with the Experience Editor for site editing and optimization.
Take this opportunity to familiarize yourself with the functionalities offered within the XM Cloud instance.










Comments
Post a Comment